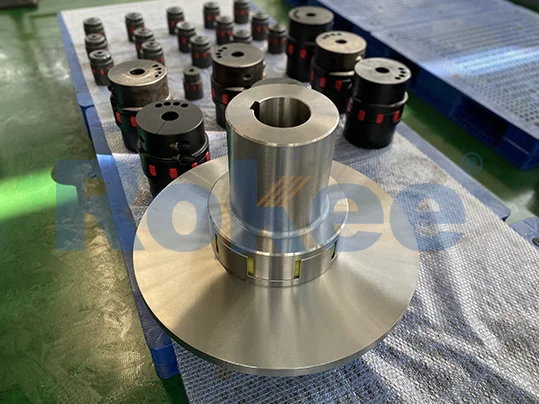
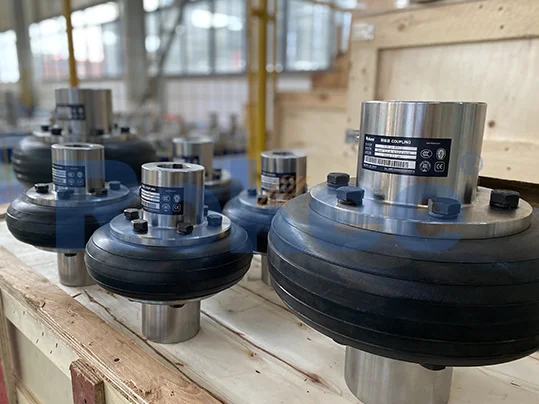
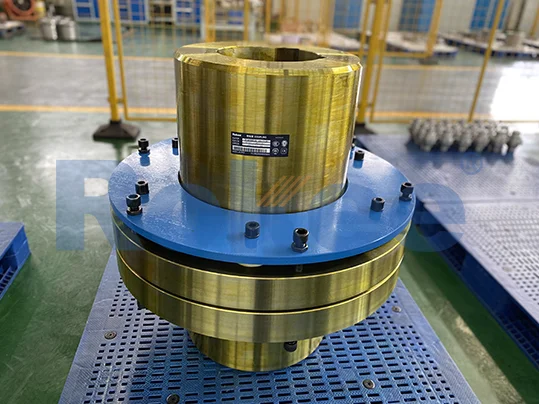
Elastic Coupling is a device used for the longitudinal joining of two rotating parts of a machine, designed to compensate for the relative displacement of the parts’ axes and to absorb the shocks caused by joining the parts. Flexible Coupling is one of the major types of couplings. They find use to connect two shafts, end-to-end in the same line to transmit power that is torque from one shaft to another, thereby causing both to rotate in unison, at the same rpm. The other purpose is to compensate for small amounts of misalignment and random movement between the two shafts.